Childhood Lead Poisoning
Prevention Program
What is lead?
- Damage to the brain and nervous system
- Slow growth and development
- Learning and behavior problems
- Hearing and speech problems
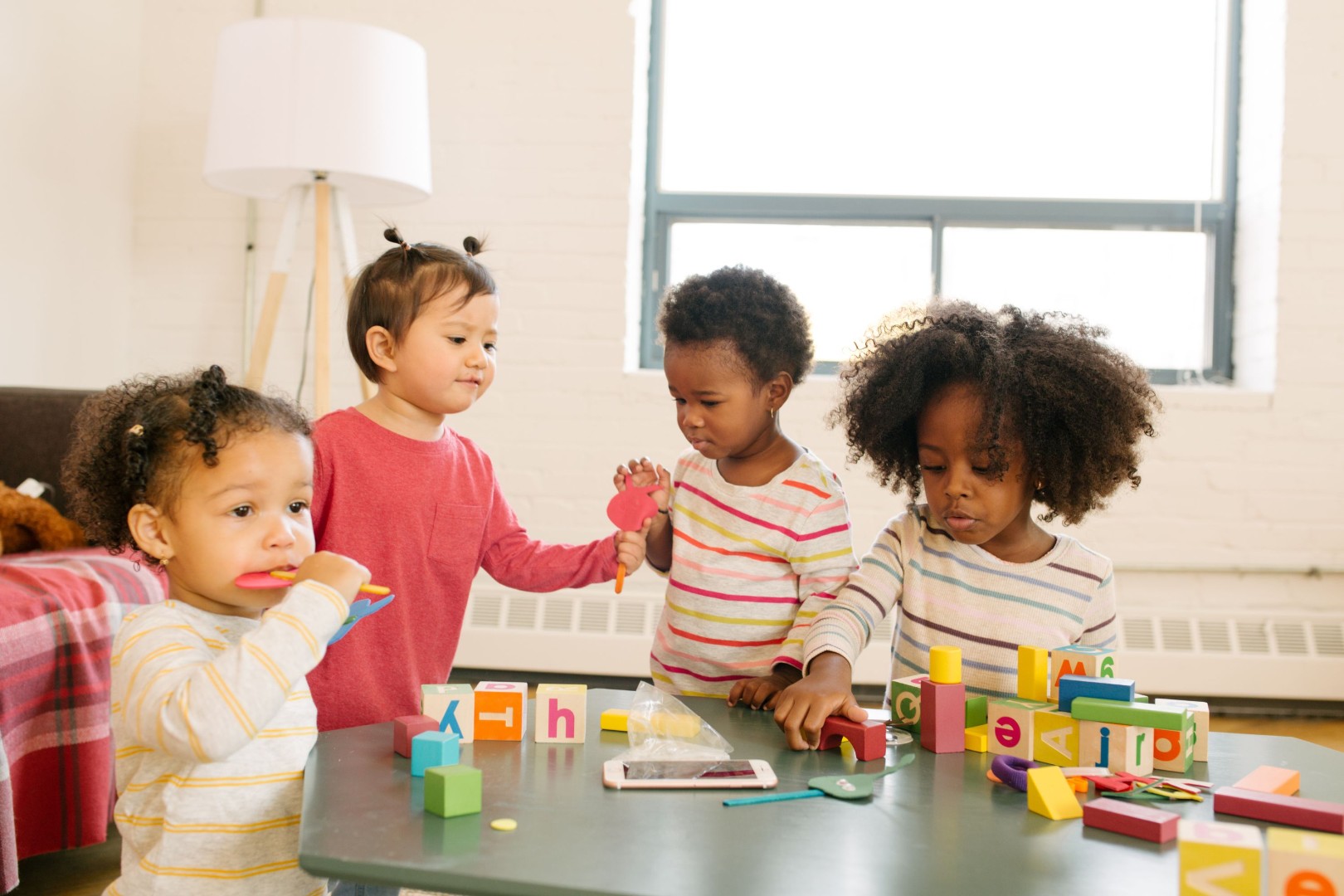

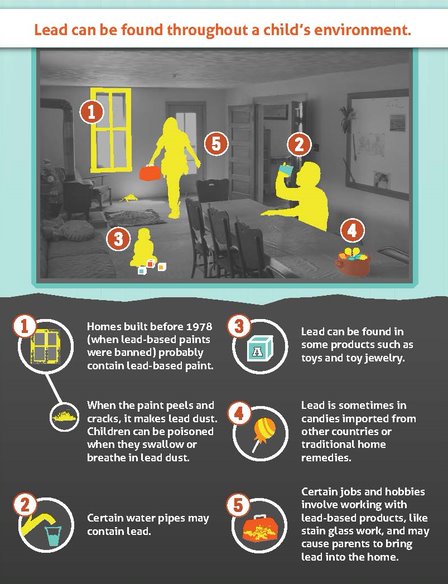
Young children under the age of 6 years are at the highest risk of lead poisoning. Their bodies absorb more lead. They often put their hands and objects into their mouths. Keep items that might contain lead out of reach.
What you can do!
Offer a variety of foods to reduce the risk of getting lead from food.
Lead can get into food through pollution in the air, water or soil. Offer different foods within each group. Instead of offering applesauce or apple juice offer apples, bananas and berries. Iron and calcium can help reduce the amount of lead absorbed by the body.
Wash hands before eating. Teach your child how to wash their hands and make a routine!

Wet Cleaning
Lead dust hates water. Clean wet, breathe safe. Watch this video:
El Polvo de ploma odia el agua. Limpie mojado, respire seguro. Mire este video:
Vacuuming
Vacuuming might not be glamorous....but using a HEPA filter makes a BIG difference for your air quality! Watch the video:
Aspirar puede que no sea glamuroso...¡pero usar un filtro HEPA hace una GRAN diferencia en la calidad del aire! Mire el video:
There is no safe level of lead in blood
Parents or caregivers who are concerned that their child may have been exposed to lead can contact their child's healthcare provider or you can chick if your child needs a lead test by visiting: Does my child need a lead test?


 Launch the media gallery 1 player
Launch the media gallery 1 player